The Covid-19 mRNA vaccines administered to billions of people across the world have raised multiple concerns, including identification of poor manufacturing practices. It is hardly surprising then, that a group of experienced geneticists have identified significant DNA contamination in both Pfizer and Moderna vaccine vials.
A team led by Kevin McKernan investigated a total of 12 vials of Moderna and Pfizer including both bivalent and monovalent product. Varying levels of contaminating plasmid DNA were detected in every vial, in addition to the intended mRNA, exceeding safety standards set by both European Medicines Agency (EMA) and Food & Drug Administration (FDA).
An 11 April 2023 preprint publication describes in detail the scientific processes undertaken in this work, which is not accessible reading for most. World Council for Health have written an excellent summary and interpretation of the conclusions, at Red Line Crossed: DNA Contamination of mRNA “Vaccines” Poses Risk to Everyone on the Planet which we highly recommend as a basic introduction to the topic. They outline the role of plasmids, responsible for the DNA contamination, in the product manufacturing process; the threats posed to human health by DNA contamination of these injectable products; ways in which those potentially exposed can optimise their health; and they call for an immediate stop to the “vaccination program”.
In this summary we do our best to break down the science for everyone to understand. This was assisted by a scientific presentation by molecular biologist/immunologist, Dr Laura Braden in March 2023 in which she referenced a Pfizer promotion published in the New York Times in April 2021. Professor Sucharit Bhakdi also presented on the topic with Dr Meryl Nass and Dr Michael Palmer at Good Morning CHD on 11 May 2023.
Transcription and Translation
Proteins provide many functions in the human body, such as forming the structure of cells, tissues, hormones and enzymes. They are continually repaired and replaced throughout the lifespan.
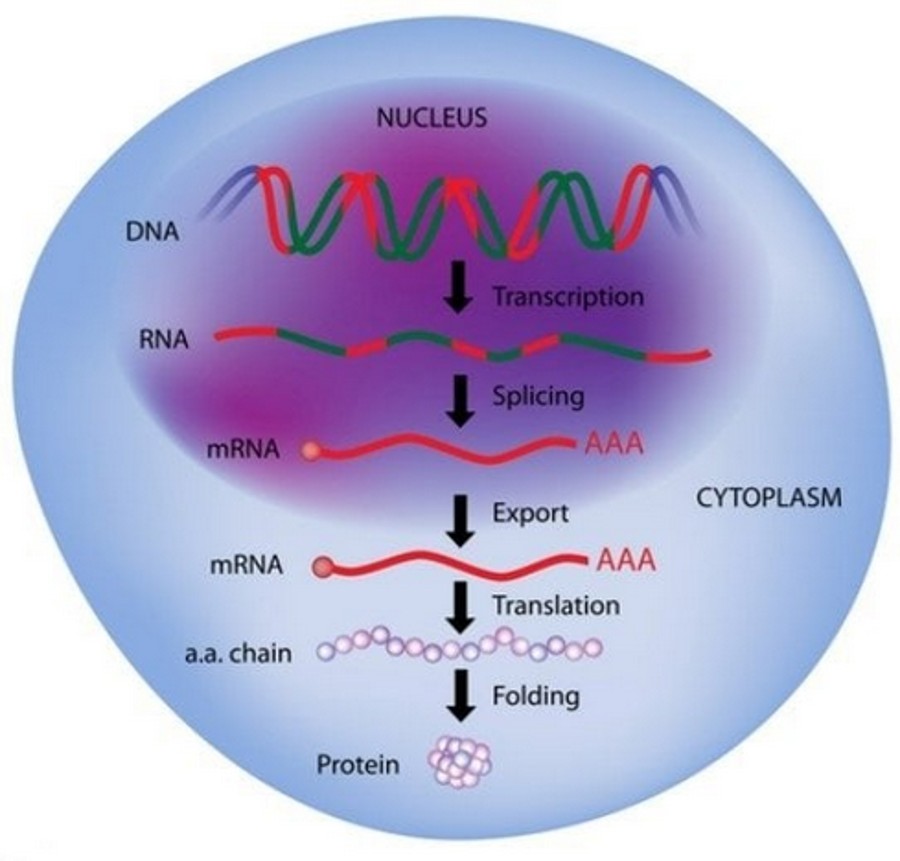
In order to make a protein, human double-stranded DNA in the nucleus of the cell is transcribed into single-stranded RNA. The RNA is then spliced into ‘messenger RNA’ (mRNA), which is transported from the cell nucleus and into the cytoplasm (the part of the cell outside of the nucleus). Here the mRNA is used as a blueprint for making amino acid chains, which then combine to form protein.
Protein in the body is used for structure (e.g. skin) and for function (e.g. enzymes to help us make energy from food, the right hormones at the right time). The body functions on protein made based on our DNA via RNA. Because of these extremely important functions, mRNA transcription and protein synthesis are tightly controlled processes in the cell, with many checks and balances to ensure fidelity.
These processes are known as transcription (DNA transcribes to RNA) and translation (RNA translates to protein), shown in simplified form in the illustration below. Understanding this helps to explain the use of plasmids in pharmaceutical manufacture.
What is a Plasmid?
Plasmids are circular DNA parcels used by bacteria in nature to exchange information. They originate from and live in bacteria, are highly transmissible and can replicate independently (“replication competent”).
Characteristics of plasmids
- Their natural habitats are bacteria and archaea (single celled organisms).
- They are replication competent.
- They often contain genes which help bacteria survive, eg antibiotic resistance is obtained from the bacterial plasmid.
- The double stranded DNA of plasmids makes them stable, meaning they do not degrade easily but they do replicate easily.
Use of plasmids in pharmaceutical product manufacture
Plasmids are commonly used in molecular biology to replicate (clone) a gene of interest. They are also used in the manufacture of certain pharmaceutical products. They can be used to transfer pieces of foreign genetic material into cells.
To produce a protein for pharmaceutical manufacturing purposes, molecular biologists take the piece of DNA they want, eg DNA of the spike protein, and use molecular scissors (enzymes) to cut the gene out of the DNA and then insert it into the plasmid, using molecular glue (enzymes). The plasmid is then inserted into the bacteria using a process known as transformation which enables rapid growth and replication.
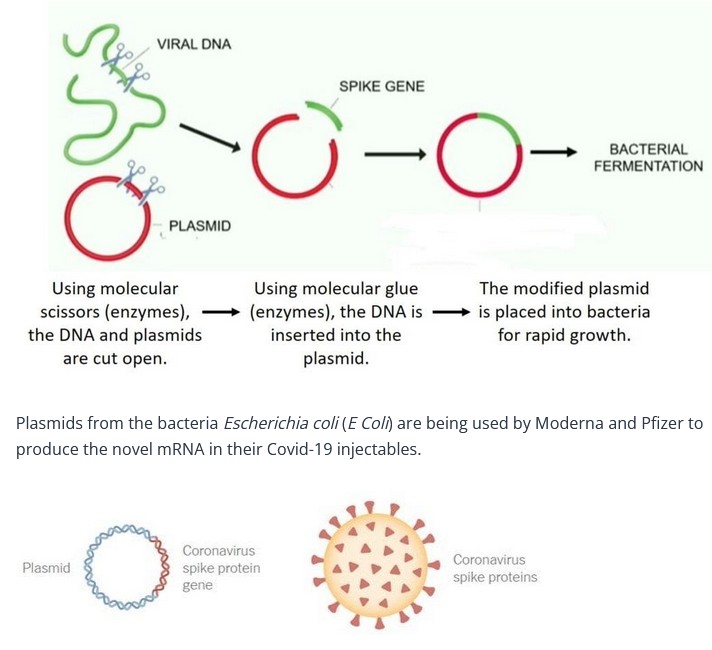
The spike-gene-modified plasmids are transferred into E Coli bacteria and grown rapidly (fermented) in large vats of nutrient-rich media. After amplification bacteria are then broken apart (ie lysed), to harvest the plasmids. The spike genes (now in billions of copies) are removed from the plasmids and cut into straight segments, a process called “linearisation”.
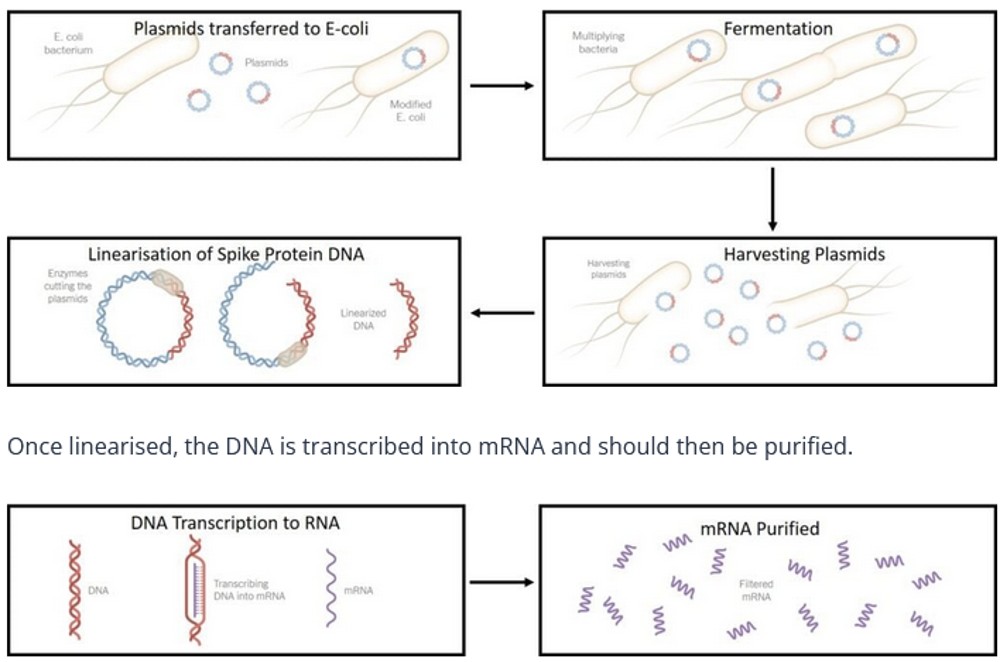
From there, further steps complete the manufacture process such as adding the lipids and enveloping the mRNA into lipid nanoparticle parcels, preparing the mixtures, removing all impurities, preparing the vials and bottling the final solution. Intense and rigorous testing is required at each step to ensure there is no contamination and that the product meets all quality standards.
Under normal good manufacturing practices, upon completion of mRNA production all plasmids would be filtered out to ensure no DNA contamination in the final product.
Detection of DNA Contamination in Pfizer and Moderna Vials
McKernan et al detected plasmids in 100% of the vials they examined. The plasmids were wrapped in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) used to transport the genetic material to human cells. LNPs are highly efficient at transporting substances throughout the body including to cells in all organs, across the blood-brain barrier, across the placental barrier and into breastmilk.

From there, further steps complete the manufacture process such as adding the lipids and enveloping the mRNA into lipid nanoparticle parcels, preparing the mixtures, removing all impurities, preparing the vials and bottling the final solution. Intense and rigorous testing is required at each step to ensure there is no contamination and that the product meets all quality standards.
Under normal good manufacturing practices, upon completion of mRNA production all plasmids would be filtered out to ensure no DNA contamination in the final product.
Detection of DNA Contamination in Pfizer and Moderna Vials
McKernan et al detected plasmids in 100% of the vials they examined. The plasmids were wrapped in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) used to transport the genetic material to human cells. LNPs are highly efficient at transporting substances throughout the body including to cells in all organs, across the blood-brain barrier, across the placental barrier and into breastmilk.

In his interview below with Veronika Kyrylenko, Canadian physician Dr Mark Trozzi rightly describes events playing out as a violent crime. While it seems the injections and those behind them get darker every day, knowledge is power and we the people need to use it.
(Click on the image below to play the video at rumble.com).
Watch: Severe Risks of DNA Contamination of mRNA Covid Shots
The NZDSOS media team extend our warm appreciation to Dr Laura Braden for her assistance in proof reading / editing this article.
SOURCE
https://nzdsos.com/2023/05/19/dna-contamination-mrna-vaccines/


